Error handling and logging
Custom exceptions
AIIDA defines a set of custom exceptions in the errors package to handle various error conditions. When extending AIIDA, it is recommended to create your own custom exceptions instead of relying on built-in ones (e.g., EntityNotFoundException) or re-throwing them directly.
REST API
Exception handler
The REST API includes a global exception handler that intercepts all exceptions raised during request processing. It translates them into appropriate HTTP responses with corresponding status codes and error messages.
Input validation
Where possible, the REST API enforces strong typing for input parameters (e.g., UUID for entity identifiers). If a parameter cannot be converted to the expected type, the API returns a 400 Bad Request response.
For more complex inputs, it is recommended to implement dedicated converters or validators to ensure that invalid data is detected early and proper error responses are generated.
Failed to send entities
If records cannot be sent (e.g., to a broker), they are temporarily stored in the database. These records are automatically retried once the broker connection is re-established. A cleanup job periodically removes records that could not be delivered within a configurable retention period.
Permission expiration
Streaming for a given permission automatically stops when the permission expires.
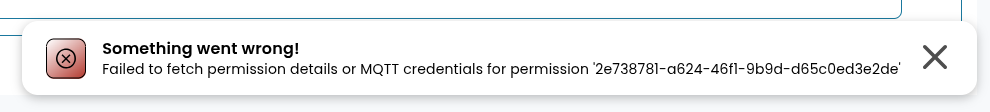
Errors in the UI
When an error occurs in the UI, a clear and user-friendly message is displayed to the user.
Logging
AIIDA uses SLF4J (Simple Logging Facade for Java) for logging, allowing flexible configuration and integration with different logging frameworks. The logging behavior can be adjusted in the application.yml file or via environment variables.
By default, the root logging level is set to INFO. You can modify it by setting the logging.level.root property to another level, such as DEBUG, WARN, or ERROR.